###############################
# 1. Left-truncated Cox model
###############################
library(survival)
# 'entry' is delayed entry time, 'end' is event/censor time, 'status' is 0/1
cox_fit <- coxph(Surv(entry, end, status) ~ covariate, data = df_left)
summary(cox_fit) # modifies risk sets for delayed entry
###############################
# 2. Interval-censored data
###############################
library(IntCens)
# Fit a proportional hazards (PH) model to interval-censored data
# L, R define the interval (L_i, R_i], Z includes covariates
PH_fit <- icsurvfit(L = df_ic$L, R = df_ic$R, Z = df_ic[, c("x1", "x2")],
model = "PH")
PH_fit$beta # estimated covariate effects
PH_fit$var # variance-covariance matrixChapter 7 - Left Truncation and Interval Censoring
Slides
Lecture slides here. (To convert html to pdf, press E \(\to\) Print \(\to\) Destination: Save to pdf)
Chapter Summary
When subjects enter the study late (thus excluding earlier failures) or when event times are only known to lie in intervals, traditional survival analysis methods must be adapted. Left truncation biases sampling toward individuals who have “survived” long enough to enroll. Interval censoring arises when event times are only observed through periodic assessments, leading to coarser information about the exact time of occurrence. It is important to properly adjust the risk sets and/or likelihood functions to ensure valid inference.
Left truncation
Left truncation occurs if a subject is enrolled at a later time \(T_L\) than the starting point so those who fail prior to \(T_L\) are never observed. Common examples include:
- Retrospective cohorts, where one must have survived long enough to be identified.
- Hospital-based registries, where patients must be alive/available to visit a center.
To correct for this bias, standard risk-set calculations in the Kaplan–Meier, log-rank test, or Cox model are modified: \[ n_j \;=\;\sum_{i=1}^{n} I\bigl(T_{Li} \;\le\; t_j \;\le\; X_i\bigr), \] so that a subject only “enters” the risk set at \(T_{Li}\). Likewise, the partial likelihood in the Cox model replaces \(I(X_j \ge t)\) with \(I(T_{Lj} \le t \le X_j)\) when constructing sums over at-risk individuals. Beyond these hazard-based methods, a more general approach employs a conditional likelihood factoring in \(T_i > T_{L,i}\):
\[ L_n(\theta) \;=\; \prod_{i=1}^{n} S\bigl(T_{Li}; \theta\bigr)^{-1}\, \lambda\bigl(X_i; \theta\bigr)^{\delta_i}\, S\bigl(X_i; \theta\bigr). \]
This reflects the fact that each subject is only observed if they survive beyond \(T_{Li}\).
Interval censoring
In interval-censored data, the exact failure time \(T\) is only known to lie in \((L_i, R_i]\). A straightforward likelihood for a parametric or semiparametric model with survival function \(S(t; \theta)\) is
\[ L_n(\theta) \;=\; \prod_{i=1}^{n} \Bigl\{ S\bigl(L_i;\theta\bigr) \;-\; S\bigl(R_i;\theta\bigr) \Bigr\}. \]
Each factor captures the probability that \(T_i\) falls strictly between \(L_i\) and \(R_i\). For purely nonparametric inference, one seeks the nonparametric MLE (NPMLE)—often computed via:
- Turnbull’s EM algorithm, which treats each actual \(T_i\) as missing and iteratively updates estimates of its distribution.
- Iterative convex minorant (ICM) methods that maximize the log-likelihood subject to a monotonicity constraint on the distribution function or baseline hazard.
Semiparametric models (e.g., Cox, proportional odds) introduce additional complexity because the baseline function is infinite-dimensional, but they can still be estimated via specialized EM or ICM algorithms. Although the baseline function converges slower than \(n^{-1/2}\), the finite-dimensional regression coefficients typically remain asymptotically normal under regular conditions.
Example R commands
Below is a brief illustration using base packages () for left truncation and the package for interval censoring.
In both cases, these functions account for the specialized likelihoods required. For left truncation, the start/stop syntax in survival::Surv() adjusts the risk set. For interval censoring, IntCens::icsurvfit() implements the ICM algorithms and can handle nonparametric and proportional hazards/odds models.
Conclusion
Left-truncated designs require rethinking “at-risk” sets to reflect delayed study entry. Interval-censored data, which provide only bracketed failure times, rely on non-/semiparametric maximum likelihood with algorithms tailored to partial observations. Although more computationally involved than standard right-censored methods, these adjustments ensure valid statistical inference in the presence of complex data structures.
R code
Show the code
###############################################################################
# Chapter 7 R Code
#
# This script reproduces all major numerical results in Chapter 7, including:
# 1. Analysis of left-truncated data (Channing House Study)
# 2. Analysis of interval-censored data (BMA HIV Study)
###############################################################################
#==============================================================================
# (A) Channing House Study (Left-Truncated Data)
#==============================================================================
library(survival)
library(tidyverse)
library(patchwork)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1. Read and Inspect the Channing Data
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
channing <- read.table("Data\\Channing House Study\\channing.txt")
head(channing)
# Convert gender to factor
channing$gender <- factor(channing$gender)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 2. Cox Model with Left-Truncation
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
obj <- coxph(Surv(Entry.Age, End.Age, status) ~ gender, data = channing)
summary(obj)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 3. Test Proportional Hazards Assumption (Schoenfeld Residuals)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
obj_zph <- cox.zph(obj)
obj_zph
# Plot the rescaled residuals
plot(
obj_zph,
ylab = "Gender",
xlab = "Age (years)",
lwd = 2
)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 4. Number at Risk by Gender Over Age
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Create a function to compute number at risk at each time point
t <- seq(60, 100, by = 1)
n_risk_t <- function(entry, end) {
m <- length(t)
n_j <- numeric(m)
for (j in seq_len(m)) {
n_j[j] <- sum(entry <= t[j] & t[j] <= end)
}
return(n_j)
}
# Compute n at risk by gender
nrisk <- channing %>%
group_by(gender) %>%
reframe(n_j = n_risk_t(Entry.Age, End.Age)) %>%
add_column(t = rep(t, 2), .before = 1) %>%
mutate(gender = if_else(gender == 1, "Male", "Female"))
# Plot number at risk
nrisk_fig <- nrisk %>%
ggplot(aes(x = t, y = n_j)) +
geom_step(aes(linetype = gender)) +
theme_bw() +
labs(
x = "Age (years)",
y = "Number at risk"
) +
theme(
legend.title = element_blank(),
legend.position = "top"
)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 5. Conditional Survival Functions Given Age 70
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
t0 <- 70
beta <- obj$coefficients
Lambda0 <- basehaz(obj, centered = FALSE)
# Subset baseline hazard for times >= t0
Lambda0t0 <- Lambda0[Lambda0$time >= t0, ]
# Re-center the hazard to start at 0 for t >= t0
Lambda0t0$hazard <- Lambda0t0$hazard - Lambda0t0$hazard[1]
# Construct survival curves for "Male" (reference) and "Female"
surv_t0 <- Lambda0t0 %>%
mutate(
St = exp(-hazard),
gender = "Male"
) %>%
add_row(
Lambda0t0 %>%
mutate(
St = exp(-hazard * exp(beta)),
gender = "Female"
)
)
# Plot conditional survival functions
surv_fig <- surv_t0 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = time, y = St)) +
geom_step(aes(linetype = gender)) +
theme_bw() +
labs(
x = "Age (years)",
y = "Conditional survival probabilities"
) +
theme(
legend.title = element_blank(),
legend.position = "top"
) +
scale_x_continuous(expand = expansion(c(0, 0.05)))
# Combine number-at-risk and conditional-survival plots
chan_model <- nrisk_fig + surv_fig +
plot_layout(ncol = 2, guides = "collect") &
theme(legend.position = 'top')
chan_model
# Uncomment to save the figure:
# ggsave("trunc_chan_model.pdf", chan_model, width = 8, height = 4)
# ggsave("trunc_chan_model.eps", chan_model, width = 8, height = 4)
#==============================================================================
# (B) Bangkok Metropolitan Administration (BMA) HIV Study (Interval-Censored)
#==============================================================================
# devtools::install_github("lmaowisc/IntCens")
library(IntCens)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1. Read BMA HIV Study Data
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
df <- read.table("Data//Bangkok Metropolitan Administration HIV_AIDS Study//bam.txt")
df
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 2. Fit Proportional Hazards Model for Interval-Censored Data
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PH_fit <- icsurvfit(
L = df$L, # left endpoint of interval
R = df$R, # right endpoint of interval
Z = df[, 3:7], # covariates
model = "PH"
)
PH_fit
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 3. Construct Table 7.3: Hazard Ratio & 95% CI
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
beta <- PH_fit$beta
se <- sqrt(diag(PH_fit$var))
c1 <- round(exp(beta), 2)
c2 <- paste0(
"(",
round(exp(beta - 1.96 * se), 2),
", ",
round(exp(beta + 1.96 * se), 2),
")"
)
noquote(cbind(c1, c2))
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 4. Predict HIV Sero-Negative Probabilities
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
par(mfrow = c(1, 1))
age.med <- median(df[, "age"])
# Plot for a median-aged male IDU (sex=1) with no needle sharing or drug injection in jail
plot(
PH_fit,
z = c(age.med, 1, 0, 0, 0),
xlim = c(0, 50),
lty = 2,
xlab = "Time (months)",
ylab = "HIV sero-negative probabilities",
lwd = 2,
main = ""
)
plot(
PH_fit,
z = c(age.med, 1, 0, 1, 0),
xlim = c(0, 50),
add = TRUE,
lwd = 2
)
legend(
"bottomleft",
lty = c(2, 1),
legend = c("No history of imprisonment", "History of imprisonment"),
lwd = 2
)Follow-up Plots
Visualization of subject-level follow-up under left truncation or interval censoring must account for the nonzero entry time or the imprecise location of the endpoint. This makes it different from right-censored data. To show the additional information, we need additional features on the plot.
Under left truncation
For each subject, we use a line segment to represent the period \([T_{Li}, X_i]\) on study, at the end of which the outcome event is distinguished from censoring by point shape.
The following is an example using the Channing House study.
library(tidyverse)
# read in the Channing study data
channing <- read.table("Data\\Channing House Study\\channing.txt")
# head(channing)
# take a random sample of 100 females
set.seed(2024)
channing_f_sub <- channing |>
filter(gender == 2) |>
sample_n(100)
# take all males
channing_m_sub <- channing |>
filter(gender == 1)
# combine the sub-samples
channing_sub <- channing_f_sub |> add_row(channing_m_sub)
n <- nrow(channing_sub) # number of subjects in the sub-sample
# panel labeller
gender_labeller <- c("1" = "Males", "2" = "Females")
# follow -up plot
chan_fig <- channing_sub |>
add_column(ID = 1 : n) |> # add an ID column as y-axis
ggplot(aes(y = reorder(ID, End.Age))) + # order subject ID shown on y-axis by end time
geom_linerange(aes(xmin = Entry.Age, xmax = End.Age)) + # line range (T_L, X)
geom_point(aes(x = Entry.Age, shape = "2"), fill = "white", size = 2) + # entry point (2)
geom_point(aes(x = End.Age, shape = factor(status)), fill = "white", size = 2) +
# endpoint (1: event; 0: censoring)
geom_vline(xintercept = 60, linewidth = 1) + # start line at age 60
facet_wrap(~ gender, ncol = 2, scales = "free", # by gender
labeller = labeller(gender = gender_labeller)) +
theme_minimal() +
scale_y_discrete(name = "Subjects") +
scale_x_continuous(name = "Age (years)", limits = c(60, 100),
breaks = seq(60, 100, by = 10),
expand = expansion(c(0, 0.05))) +
scale_shape_manual(limits = c("2", "0", "1"), values = c(22, 23, 19),
labels = c("Admission", "Censoring", "Death")) + # set the point shapes
theme( # theme formatting
legend.position = "top",
legend.title = element_blank(),
axis.text.y = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.y = element_blank(),
panel.grid.major.y = element_blank(),
legend.text = element_text(size = 11),
axis.title = element_text(size = 11),
axis.text = element_text(size = 10),
strip.text = element_text(size = 10)
)
chan_fig
# ggsave("trunc_chan_fig.pdf", chan_fig, width = 8, height = 9)
# ggsave("trunc_chan_fig.eps", chan_fig, width = 8, height = 9)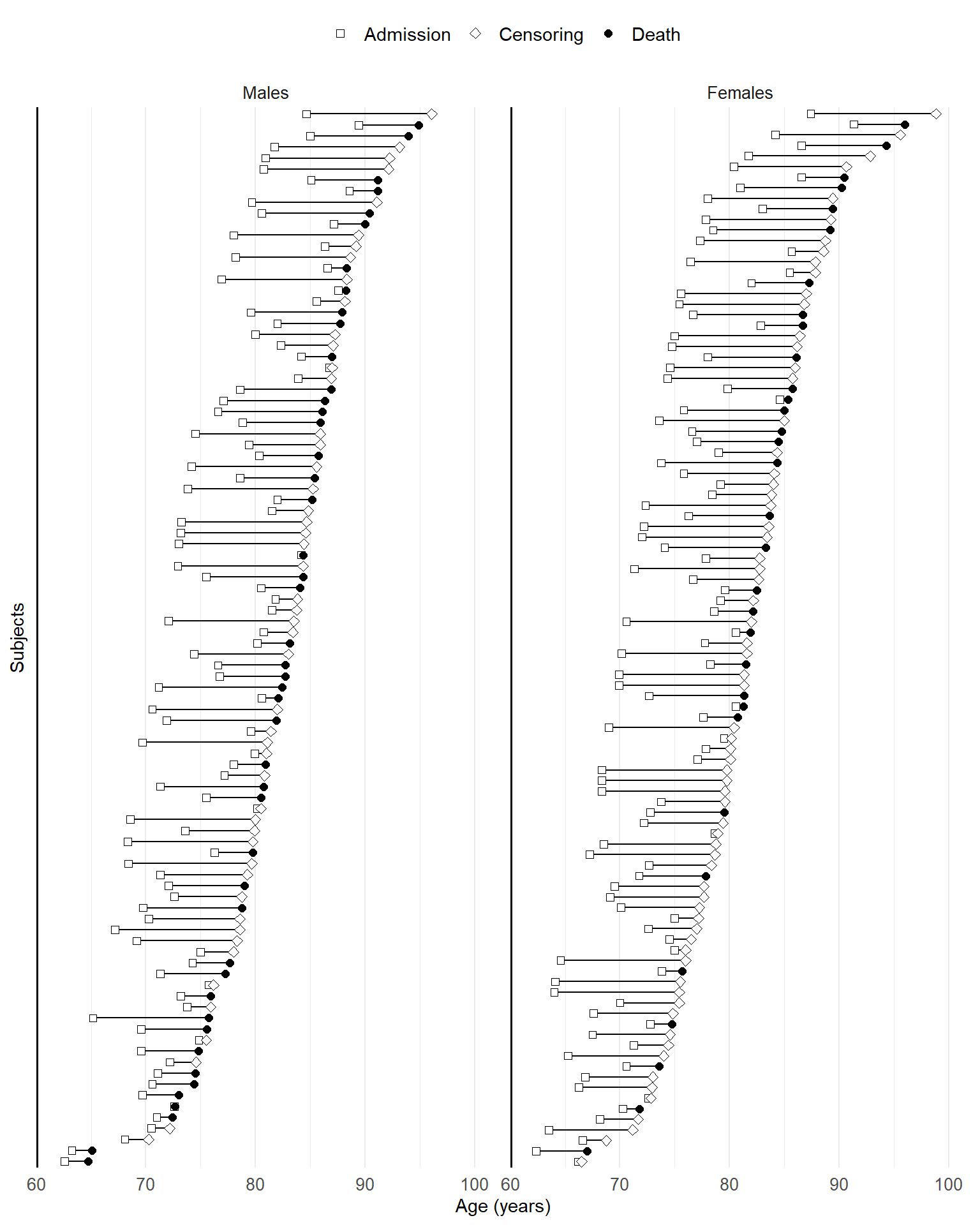
Under interval censoring
For each subject, we use a gray line to represent the follow-up period. The check-up times can be marked on it by dots if such data are available. The event-containing interval \([L_i, R_i]\) (\(R_i<\infty\)) is highlighted from the rest of the follow-up period using a black line segment.
The following is an example using the Bangkok Metropolitan Administration HIV study.
library(IntCens)
## BMA HIV study
## Bangkok Metropolitan Administration HIV Study
bma <- read.table("Data//Bangkok Metropolitan Administration HIV_AIDS Study//bam.txt")
# sample size
n <- nrow(bma)
# create L and R
bma_lr <- bma |>
mutate(
ID = 1 : n,
.before = 1
)
# take a random sample of 150 subjects per imprisonment status
set.seed(2024229)
bma_lr_jail_sub <- bma_lr |>
filter(jail == 1) |>
sample_n(150)
bma_lr_nojail_sub <- bma_lr |>
filter(jail == 0) |>
sample_n(150)
## combine the sub-samples
bma_lr_sub <- bma_lr_jail_sub |>
add_row(bma_lr_nojail_sub) |>
mutate(
end = ifelse(R == Inf, L, R),
status = (R < Inf) + 0 # an indicator of event occurence vs right censoring
)
# panel labeller
jail_labeller <- c("0" = "No imprisonment", "1" = "Imprisonment")
# follow -up plot
bma_fig <- bma_lr_sub |>
ggplot(aes(y = reorder(factor(ID), end))) + # order subjects by R or last check-up
geom_linerange(aes(xmin = 0, xmax = L), alpha = 0.3) + # gray line for non-event-containing period
geom_linerange(data = bma_lr_sub |> filter(status == 1),
aes(xmin = L, xmax = R), linetype = 1) + # black line for event-containing interval
geom_point(data = bma_lr_sub |> filter(status == 1), aes(x = L, shape = "1"), size = 2) +
geom_point(data = bma_lr_sub |> filter(status == 1), aes(x = R, shape = "1"), size = 2) +
geom_point(data = bma_lr_sub |> filter(status == 0), aes(x = L, shape = "0"),
fill = "white", size = 2) + # different point shapes
geom_vline(xintercept = 0) +
facet_wrap(~ jail, scales = "free", labeller = labeller(jail = jail_labeller)) +
# by imprisonment status
theme_minimal() +
scale_y_discrete(name = "Subjects") +
scale_x_continuous(name = "Time (months)",
breaks = seq(0, 48, by = 6),
expand = expansion(c(0, 0.05))) +
scale_shape_manual(limits = c("0", "1"), values = c(23, 19),
labels = c("Right censoring", "L-R containing seroconversion")) +
# set point shapes
theme( # theme formatting
legend.position = "top",
legend.title = element_blank(),
axis.text.y = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.y = element_blank(),
panel.grid.major.y = element_blank(),
legend.text = element_text(size = 11),
axis.title = element_text(size = 11),
axis.text = element_text(size = 10),
strip.text = element_text(size = 10)
)
bma_fig
# ggsave("trunc_bma_fig.pdf", bma_fig, width = 8, height = 12)
# ggsave("trunc_bma_fig.eps", bma_fig, width = 8, height = 12, device = cairo_pdf)