# Install if needed
# install.packages("npsurvSS")
library(npsurvSS)
# 1. Define arms (control vs. treatment) for a two-arm study
control <- create_arm(size = 500,
accr_time = 2, # uniform accrual over 2 years
follow_time = 3.5, # then followed 3.5 years
surv_scale = 0.174, # baseline hazard for event
loss_scale = 0.01) # hazard of loss to follow-up
treatment <- create_arm(size = 500,
accr_time = 2,
follow_time = 3.5,
surv_scale = 0.174 * 0.8, # hazard ratio = 0.8
loss_scale = 0.01)
# 2. Compute required sample size for different tests
res_size <- size_two_arm(
control,
treatment,
test = list(
list(test = "weighted logrank"), # log-rank
list(test = "rmst difference", milestone = 3), # RMST at 3 years
list(test = "rmst difference", milestone = 5) # RMST at 5 years
)
)
print(res_size)Chapter 6 - Sample Size Determination and Study Design
Slides
Lecture slides here. (To convert html to pdf, press E \(\to\) Print \(\to\) Destination: Save to pdf)
Chapter Summary
Determining an appropriate sample size is a crucial step in designing a time-to-event study. Inadequate sample size can lead to insufficient power, while an overpowered study may waste resources. As two most important methods in survival analysis, the log-rank test (or equivalently, a Cox model with a binary predictor) and restricted mean survival time (RMST) analysis need special attanetion. In their sample size calculations, study design choices—such as accrual patterns, length of follow-up, and loss to follow-up assumptions—play an important role.
General approach to sample size calculation
A common starting point is to consider a test statistic \(S_n=\sqrt n T_n /\hat\sigma_n\) that is approximately standard normal under the null hypothesis. Define a minimal clinically important effect size \(\theta\) (e.g., a targeted log-hazard ratio or a difference in RMST) and specify the desired power \(\gamma\). The general form for the required sample size, under asymptotic normality, often reduces to
\[ n \;=\; \frac{\sigma_0^2\,\bigl(z_{1-\alpha/2} \,+\, z_\gamma\bigr)^2}{f(\theta)^2}, \]
where \(f(\theta) = E(T_n)\) is the “signal” contributed by the effect size, \(\sigma_0^2\) is the variance term under the null, and \(z_{p}\) is the \(p\)-quantile of the standard normal distribution. Intuitively, stronger signals \(\bigl|f(\theta)\bigr|\) reduce the required \(n\), while higher variance \(\sigma_0^2\) or more stringent significance/power criteria increase \(n\).
Schoenfeld’s formula for the Cox (log-rank) test
Under a proportional hazards model with a binary treatment: \[ \lambda(t \mid Z=1) \;=\; \lambda_0(t)\,\exp(\theta), \] the log-rank test statistic has a well-known large-sample result leading to Schoenfeld’s formula:
\[\begin{equation}\label{eq:cox:sample_size} n \;=\; \frac{\bigl(z_{1-\alpha/2} + z_\gamma\bigr)^2}{q(1-q)\,\psi\,\theta^2}, \tag{1} \end{equation}\]
where:
- \(q\) is the proportion allocated to treatment,
- \(\theta\) is the log-hazard ratio (\(\theta=0\) under the null),
- \(\psi\) is the expected proportion of events (failures).
Alternatively, we can express \(n\psi\), the total number of events, as the right-hand side of \(\eqref{eq:cox:sample_size}\) without \(\psi\) in the denominator. You often hear this referred to as an “event-driven” calculation—knowing the total number of events required can be more important than total enrollment.
Sample size for RMST
The restricted mean survival time (RMST) over \([0, \tau]\) captures the average time lived up to \(\tau\). For a two-sample comparison, the difference \(\theta(\tau) = \mu_1(\tau) - \mu_0(\tau)\) can be tested, by its estimator \(\hat\theta(\tau)\). The corresponding sample size formula is:
\[\begin{equation}\label{eq:rmst:sample_size} n \;=\; \frac{\zeta(\tau)\,\bigl(z_{1-\alpha/2} + z_\gamma\bigr)^2}{ q(1-q)\,\theta(\tau)^2}, \tag{2} \end{equation}\]
where \(\zeta(\tau)\) is a variance-related term (depending on survival and censoring distributions). While slightly less efficient under strict proportional hazards, RMST-based tests offer a direct interpretation of how many additional months or years are gained under one treatment arm compared to another.
Study design and its impact
Study design considerations—uniform accrual over \(b\) years, additional follow-up \(c\) years after accrual closes, and potential exponential loss to follow-up—shape the computations of \(\psi\) (for log-rank) and \(\zeta(\tau)\) (for RMST) through the censoring distribution.
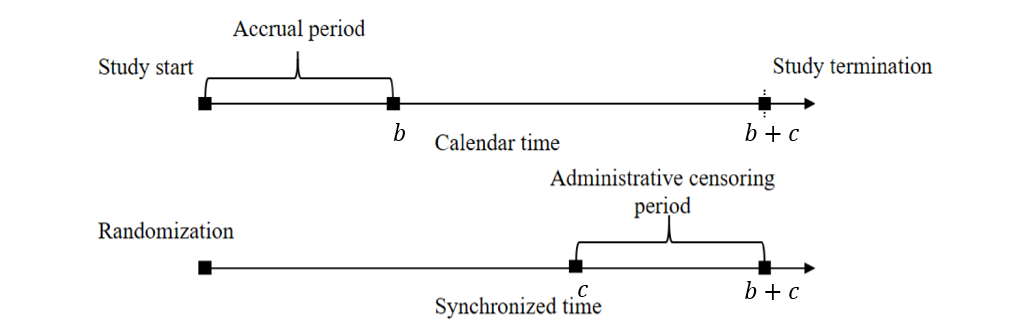
Under this set-up:
- Administrative censoring: Uniform\([c, b + c]\)
- Loss to follow-up: Assume exponential dropout with rate \(\lambda_L\).
These assumptions feed into analytic or numerical formulas to calculate:
- Censoring survival function \[\begin{equation}\label{eq:design:censoring} G(t;\lambda_L, b, c):=\mathrm{pr}(C>t)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} \exp(-\lambda_L t)& 0\leq t\leq c\\ b^{-1}(c+b-t)\exp(-\lambda_L t) & c<t<c+b \\ 0& t\geq c+b. \end{array}\right. \end{equation}\]
- \(\psi\) for log-rank (closed-form) \[\begin{equation}\label{eq:cox:psi} \psi=\frac{\lambda_0}{\lambda_0+\lambda_L}\left[1-\exp\{-(\lambda_0+\lambda_L)c\} \frac{1-\exp\{-(\lambda_0+\lambda_L)b\}}{(\lambda_0+\lambda_L)b}\right] \end{equation}\]
- \(\zeta(\tau)\) for RMST (needs numerical integration) \[\begin{equation}\label{eq:design:rmst_zeta} \zeta(\tau)=\lambda_0^{-1}\int_0^\tau\{\exp(-\lambda_0 t)-\exp(-\lambda_0 \tau)\}^2\exp(\lambda_0 t)G(t;\lambda_L, b, c)^{-1}\mathrm{d} t \end{equation}\]
- Plug \(\psi\) or \(\zeta(\tau)\) back into sample size formulas \(\eqref{eq:cox:sample_size}\) or \(\eqref{eq:rmst:sample_size}\), respectively.
A general implementation
The R package npsurvSS offers more general routines for sample size/power calculations under log-rank and RMST approaches. Suppose we hypothesize an exponential event rate \(\lambda_0\) in the control group and a hazard ratio \(\mathrm{HR} = \exp(\theta)\) in the treatment group:
You can customize the accrual pattern (piecewise uniform or otherwise), use Weibull rather than exponential survival times, or request sample size for alternative tests (e.g., Gehan–Wilcoxon, RMST ratio, survival probability difference).
Conclusion
Planning a time-to-event study involves balancing the feasibility of enrolling and following patients against the power to detect a meaningful effect. Schoenfeld’s formula under the proportional hazards framework yields intuitive “event-driven” calculations, while RMST-based approaches similarly ensure adequate power for differences in average time lived within a specified window. Because design factors—accrual, follow-up length, and dropout processes—directly enter these formulas, it is vital to specify reasonable assumptions and possibly refine them via pilot data.
R code
Show the code
###############################################################################
# Chapter 6 R Code
#
# This script reproduces all major numerical results in Chapter 6, including:
# 1. Functions for sample size calculations (psi_fun, zeta_fun)
# 2. Numerical examples from Section 6.2.2
# 3. Sample size computations for the GBC pilot data
###############################################################################
#==============================================================================
# (A) Functions Needed for Sample Size Calculation
#==============================================================================
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1. psi_fun(lambda0, lambdaL, b, c)
# Computes the event proportion psi for Cox model sample size
#
# Inputs:
# lambda0 = hazard rate for T
# lambdaL = hazard rate for LTFU
# b = length of accrual (years)
# c = additional length of follow-up (years)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
psi_fun <- function(lambda0, lambdaL, b, c) {
lambda <- lambda0 + lambdaL
psi <- lambda0 / lambda * (
1 - exp(-lambda * c) * (1 - exp(-lambda * b)) / (lambda * b)
)
return(psi)
}
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 2. zeta_fun(tau, lambda0, lambdaL, b, c)
# Computes the variance component for RMST sample size via numerical integral
#
# Inputs:
# tau = restricting time
# lambda0 = hazard rate for T
# lambdaL = hazard rate for LTFU
# b = length of accrual (years)
# c = additional follow-up (years)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Survival function for censoring
Gfun <- function(t, lambdaL, b, c) {
Gt <- ifelse(
t <= c,
exp(-lambdaL * t),
ifelse(
t < (c + b),
exp(-lambdaL * t) * (b + c - t) / b,
0
)
)
return(Gt)
}
# The integrand for zeta
zeta_integrand <- function(t, tau, lambda0, lambdaL, b, c) {
integrand <- (exp(-lambda0 * t) - exp(-lambda0 * tau))^2 *
exp(lambda0 * t) / (Gfun(t, lambdaL, b, c) * lambda0)
return(integrand)
}
# Main function using integrate()
zeta_fun <- function(tau, lambda0, lambdaL, b, c) {
f <- function(t) {
zeta_integrand(t, tau, lambda0, lambdaL, b, c)
}
zeta <- integrate(f, lower = 0, upper = tau)
return(zeta$value)
}
#==============================================================================
# (B) Numerical Results in Section 6.2.2
#==============================================================================
# Evaluate zeta_fun at specific values
zeta_fun(tau = 5, lambda0 = 0.2, lambdaL = 0.01, b = 2, c = 4)
#==============================================================================
# (C) Sample Size Calculation Example with GBC Data
#==============================================================================
library(survival)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1. Read GBC Data
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
gbc <- read.table("Data//German Breast Cancer Study//gbc.txt")
# Sort the data by time within each id
o <- order(gbc$id, gbc$time)
gbc <- gbc[o, ]
# Keep the first row for each id
df <- gbc[!duplicated(gbc$id), ]
# Set status = 1 if status == 1 or 2
df$status <- (df$status > 0) + 0
# Subset: post-menopausal (meno==2) & no hormonal treatment (hormone==1)
pilot <- df[df$meno == 2 & df$hormone == 1, ]
n <- nrow(pilot) # n = 209, matches Table 1.12 (Chapter 1)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 2. Estimate Baseline Hazard and Setup
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
pilot$time <- pilot$time / 12 # convert months to years
lambda0 <- sum(pilot$status > 0) / sum(pilot$time) # ~0.174
# Accrual (b = 2 years), follow-up (c = 3.5 years)
lambdaL <- 0.01 # LTFU rate
b <- 2
c <- 3.5
# Compute psi and zeta at tau = 3, 5
psi <- psi_fun(lambda0, lambdaL, b, c)
zeta3 <- zeta_fun(tau = 3, lambda0, lambdaL, b, c)
zeta5 <- zeta_fun(tau = 5, lambda0, lambdaL, b, c)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 3. Sample Size Computations for Various Hazard Ratios
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HR <- seq(0.6, 0.9, by = 0.01) # hazard ratio range
lambda1 <- lambda0 * HR
# Function for difference in RMST (exponential assumption)
RMST_diff <- function(tau, lam0, lam1) {
val <- (1 - exp(-lam1 * tau)) / lam1 - (1 - exp(-lam0 * tau)) / lam0
return(val)
}
# For tau = 3 and tau = 5
theta3 <- RMST_diff(3, lambda0, lambda1)
theta5 <- RMST_diff(5, lambda0, lambda1)
# Setup for alpha = 0.05 (two-sided), power = 0.8 or 0.9
q <- 0.5
za <- qnorm(0.975)
gamma_list <- c(0.80, 0.90)
par(mfrow = c(1, 2))
for (i in seq_along(gamma_list)) {
gamma <- gamma_list[i]
zg <- qnorm(gamma)
# Sample sizes for log-rank, 3-RMST, and 5-RMST
ncox <- (za + zg)^2 / (q * (1 - q) * psi * (log(HR))^2)
nRMST3 <- zeta3 * (za + zg)^2 / (q * (1 - q) * theta3^2)
nRMST5 <- zeta5 * (za + zg)^2 / (q * (1 - q) * theta5^2)
plot(
HR, ncox,
type = "l",
lwd = 2,
ylim = c(0, 7000),
xlab = "Hazard ratio",
ylab = "Sample size",
main = paste0("Power = ", gamma),
cex.lab = 1.2,
cex.axis = 1.2
)
lines(HR, nRMST5, lty = 2, lwd = 2)
lines(HR, nRMST3, lty = 3, lwd = 2)
legend(
"topleft",
lty = 1:3,
c("Log-rank", "5-RMST", "3-RMST"),
lwd = 2,
cex = 1.2
)
}
#==============================================================================
# (D) Demonstration with npsurvSS Package (Yung and Liu, 2020)
#==============================================================================
library(npsurvSS)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1. Configure Two Arms (Control vs. Treatment)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
lambda0 <- 0.173 # baseline event hazard
lambdaL <- 0.01 # hazard rate for LTFU
control <- create_arm(
size = 500,
accr_time = 2,
follow_time= 3.5,
surv_scale = lambda0,
surv_shape = 1, # default
loss_scale = lambdaL,
loss_shape = 1
)
lambda1 <- lambda0 * 0.8
treatment <- create_arm(
size = 500,
accr_time = 2,
follow_time= 3.5,
surv_scale = lambda1,
loss_scale = lambdaL
)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 2. Compare Required Sample Sizes for Several Tests
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
size_two_arm(
control,
treatment,
test = list(
list(test = "weighted logrank"), # Log-rank test
list(test = "rmst difference", milestone = 3), # RMST at 3 years
list(test = "rmst difference", milestone = 5) # RMST at 5 years
)
)
# Alternatively, power calculations could be done via power_two_arm()
# power_two_arm(control, treatment)